leetcode题目
有序列表转二叉查找树-109
Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
二叉树的最小深度-111
最小深度:根节点到某个叶子节点的最短路径。
- 为空,返回0
- 左孩子为空,则结果在右孩子
- 右孩子为空,则结果在左孩子
- 左右均不为空,返回小的+1
二叉树遍历
先序遍历-144
Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
根、左、右。栈。
- 先把根节点入栈
- 栈不为空时,出栈一个元素
- 访问该元素,右孩子进栈,左孩子进栈。 因为出栈,先出左孩子,再出右孩子。
vector<int> pre_order(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> vpre;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if (root != nullptr) {
st.push(root);
}
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* p = st.top();
vpre.push_back(p->val);
st.pop();
// 右进、左进;出时:左先出
if (p->right) {
st.push(p->right);
}
if (p->left) {
st.push(p->left);
}
}
return vpre;
}中序遍历-094
思路
左、根、右。使用栈。
- p=root
- p不为空,p入栈,一直向左走
p = p.left,扫描它的左孩子,所有左孩子依次入栈 - p为空时,
p = st.top(),p位于栈顶,显然没有左孩子或者左孩子已经遍历过,p访问出栈。 - 扫描右孩子
p = p.right
从根节点开始,一直向左,所有的左孩子入栈, 出栈一个节点,访问,它的右孩子入栈。
vector<int> inorder_traversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* p = root;
while (p || !st.empty()) {
if (p) {
// 根节点入栈
st.push(p);
// 扫描左孩子
p = p->left;
} else {
// p位于栈顶,左孩子已经被遍历过或者没有左孩子,直接出栈访问
p = st.top();
res.push_back(p->val);
st.pop();
// 扫描右孩子
p = p->right;
}
}
return res;
}后序遍历-145
Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
思路
左孩子、右孩子、根节点。使用栈。使用pre记录上一次遍历的节点。
- 根节点入栈
- 栈不为空,访问栈顶元素p
- 直接访问p的条件:p没有左右孩子 or 左右孩子刚刚遍历结束,只要pre是左或者右孩子即可
- p可以直接访问,则访问出栈
- p不能直接访问,则左右孩子入栈
vector<int> post_order(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
// 前一次访问的节点
TreeNode* pre = nullptr;
if (root != nullptr) {
st.push(root);
}
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* p = st.top();
// 0. 检查是否可以直接访问p
bool no_child = (p->left == nullptr && p->right == nullptr);
bool pre_is_child = (pre == p->left || pre == p->right);
if (nullptr == pre) {
pre_is_child = false;
}
// 1. p无左右子树 or 左右子树刚刚遍历完,直接访问p
if (no_child || pre_is_child) {
res.push_back(p->val);
pre = p;
st.pop();
}
// 2. 需要将p的左右孩子入栈
else {
if (p->right) {
st.push(p->right);
}
if (p->left) {
st.push(p->left);
}
}
}
return res;
}层次遍历-102
层次遍历,使用队列。
从上到下 Binary Tree Level Order Traversal 和从下到上 Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II。
如果只需要顺序放在一个数组里面,则不需要分层,直接层次遍历即可。
但是此题,需要分层构建vector。
数量记录思路
不是很好。
- 队列层次遍历
- 当前层在队列中的数量:
cur_remain - 下一层的数量:
next_level cur_remain == 0时, 就切换到下一层
[关键代码]
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (root == nullptr) {
return res;
}
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
res.push_back(vector<int>());
// 当前层,在队列里面的元素数量
int cur_remain = 1;
// 下一层的元素数量
int next_level = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* now = q.front();
q.pop();
// 存入队列
res[res.size() - 1].push_back(now->val);
// 左右孩子入队
if (now->left) {
q.push(now->left);
next_level++;
}
if (now->right) {
q.push(now->right);
next_level++;
}
// 当前层数量--
cur_remain--;
// 切换到下一层
if (cur_remain == 0 && !q.empty()) {
res.push_back(vector<int>());
cur_remain = next_level;
next_level = 0;
}
}
return res;
}一次遍历一层的思路
很好,掌握!
- 一次while循环,保证当前队列里面只有当前层的元素,用vector记录当前层的序列
q.size()获得当前层元素数量,然后本次循环,只从队列里面出这么多元素。- 依次遍历当前层的所有元素,出队,同时左右孩子入队
- q为空,则所有层遍历结束
/*
* 保证当前队列的循环只有当前层的
*/
vector<vector<int>> level_order(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (root == nullptr) {
return res;
}
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
// 一次while循环,出掉当前层的所有元素,下一层的元素全部入队
while (!q.empty()) {
// 当前层的数量和遍历结果序列
int level_num = q.size();
vector<int> curv;
for (int i = 0; i < level_num; i++) {
TreeNode* p = q.front();
// p的左右孩子入队列
if (p->left) q.push(p->left);
if (p->right) q.push(p->right);
// p出队,放到当前层的vector中
q.pop();
curv.push_back(p->val);
}
// 放到末尾,就是从下到上
// res.insert(res.begin(), curv);
res.push_back(curv);
}
return res;
}发现重复的数字-287
Find the Duplicate Number, 类似于aim2offer中查找重复的数字
数组a,有n+1个数,都在[1,n]范围内,只有一个重复的元素。找到它
二分思路
[1, n]这个范围有n个数。划分为两个范围[1, m]和[m+1, n]
- 每次去遍历整个数组,统计两个范围内的数字的数目
- 统计整个数组中元素在
[1, m]范围内的个数 - 统计整个数组中元素在
[m+1, n]范围内的个数
[1, m]这m个数字的数量是c
- 如果
c > m, 则1, m]内一定存在重复的数,e = m - 否则,
[m+1, n]一定存在重复的数,s = m + 1
/*
* 找到一个重复的数字
* Args:
* a -- 数组,n+1个元素,范围[1,n],至少有一个重复的数字
* Returns:
* dup -- 重复的数字
*/
int find_duplicate(const vector<int>& a) {
int n = a.size() - 1;
if (n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int l = 1;
int r = n;
int dup = -1;
// 不断缩小范围
while (l <= r) {
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
// 统计[l,m]在a中的出现次数
int count = count_range(a, l, m);
if (l == r) {
if (count >= 2) {
dup = l;
break;
}
}
// [l, m]有重复的
if (count > (m - l + 1)) {
r = m;
}
// [m+1, r]有重复的
else {
l = m + 1;
}
}
return dup;
}
/*
* 找到数组a中,[min, max]这些数的出现次数
*/
int count_range(const vector<int>& a, int min, int max) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) {
if (a[i] >= min && a[i] <= max) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}合并两条有序链表-021
Merge Two Sorted Lists ,和归并排序的Merge操作 很类似。
考虑鲁棒性
思路
与 若有一个为空的,则返回另一个 - 初始化新的head,选择
与 中第一个节点较小的那个 - while循环,谁小选谁
- 结束之后,直接把未空的链表链接上即可
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
if (l1 == nullptr) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 == nullptr) {
return l1;
}
// 初始化head
ListNode* head = nullptr;
if (l1->val < l2->val) {
head = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
} else {
head = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
// 遍历两条链表,每次选择小的追加到p的后面
ListNode* p = head;
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1->val < l2->val) {
p->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
} else {
p->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
p = p->next;
}
// 某一条链表还有剩余
if (l1) {
p->next = l1;
}
if (l2) {
p->next = l2;
}
return head;
}合并多条有序链表-023
我们已经会合并2条链表了,可以使用归并排序和二分查找的思想来合并多个列表。
示例
现在有1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6条链表
- 第一步:
1-6,2-5,3-4合并,得到新的1, 2, 3 - 第二步:
1-3合并,2不动,得到新的1, 2 - 第三步:
1-2合并, 得到新的2, 合并完成 - 返回
list[0]
总结
- 直到
len==1合并到只有一条链表,合并到list[0] - 对于当前len,折半两两合并,
i和len-i-1合并,放到前面lists[i] - len缩减一半,
len=(len+1)/2
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
if (lists.empty()) {
return nullptr;
}
int len = lists.size();
// 直到只有一条链表
while (len > 1) {
// 依次合并前后两条链表
for (int i = 0; i < len / 2; i++) {
// 合并放到list[i]
lists[i] = mergeTwoLists(lists[i], lists[len - i - 1]);
}
len = (len + 1) / 2;
}
return lists[0];
}Z型打印二叉树-103
Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
参考层次遍历 一次遍历一层的思路。
- 一次遍历一层,得到当前层的遍历结果
- 单数,从左向右;偶数,从右向左
- 每次遍历一个元素,把左右孩子入队
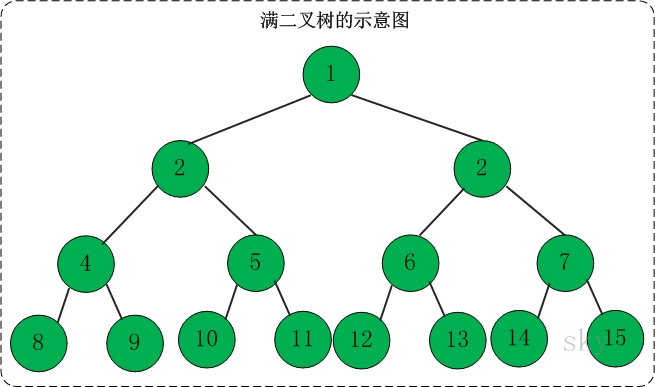
- 根节点,向右走
- 第二层,向左走
- 向右走,从队头出,孩子先左后右,加到队尾
- 向左走,从队尾出,孩子先右后左,加到队首
两个栈的思路
栈1初始存放根节点,栈2为空
- 向右走,栈1全部出栈,先左后右孩子依次压入栈2,栈底-栈顶,栈2为
2 3 - 向左走,栈2全部出栈,先右后左孩子依次压入栈1,栈1为
7 6 5 4 - 向右走,栈1出栈,左右孩子依次压入栈2,栈2为
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 - 向左走,栈2出栈,结束
/*
* 使用两个栈z型层次打印二叉树
*/
vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (root == nullptr) {
return res;
}
stack<TreeNode*> st1;
stack<TreeNode*> st2;
st1.push(root);
while (!st1.empty() || !st2.empty()) {
// 向右走
vector<int> curv;
if (!st1.empty()) {
while (!st1.empty()) {
TreeNode* p = st1.top();
st1.pop();
curv.push_back(p->val);
if (p->left) st2.push(p->left);
if (p->right) st2.push(p->right);
}
}
// 向左走
else {
while (!st2.empty()) {
TreeNode* p = st2.top();
st2.pop();
curv.push_back(p->val);
if (p->right) st1.push(p->right);
if (p->left) st1.push(p->left);
}
}
res.push_back(curv);
}
return res;
}二叉树路径求和-112.113.437
题目1 从根节点到叶子求和-112
Path Sum, EASY
给一颗二叉树和一个sum值,判断是否有从根节点到叶子节点的路径,使得路径上的节点求和等于sum
思路
做减法
- 根节点为空,False
- 没有孩子,判断
root.val == sum - 有孩子,把sum减掉根节点的值,去判断左右子树是否有 ,
sum = sum - root.val
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
// 1. 节点为空
if (root == nullptr) {
return false;
}
// 2. 没有左右子树,直接判断
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
return root->val == sum;
}
// 3. 减小sum,去递归判断左右子树
int newsum = sum - root->val;
return hasPathSum(root->left, newsum) || hasPathSum(root->right, newsum);
}题目2 从根节点到叶子节点求和-保存路径-113
Path Sum-113, Medium
给二叉树和sum值,找到root-to-leaf的路径,使得和为sum。保存该路径
思路
用vector<int> path 来记录当前路径, vector<vector<int>> res 记录最终结果
- 根节点为空,返回
- 到达叶子节点,
val == sum, 把当前节点加入path,当前path加入res, 否则返回 - 非叶子节点,把当前节点加入path,去左右子树中遍历,继续追加path直到叶子节点
- 非叶子节点,结束后,把当前节点从path中删除
/*
* 找到树种从root到leaf的所有和为sum的路径
*/
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (root == nullptr) {
return res;
}
vector<int> path;
find_path(root, sum, path, res);
return res;
}
/*
* 递归遍历节点,逐渐添加节点到当前的path,叶子节点,满足要求时,则把path追加到res中
* Args:
* root -- 当前节点
* path -- 当前路径
* res -- 所有路径
* Returns:
* None
*/
void find_path(TreeNode* root, int sum, vector<int>& path, vector<vector<int>> &res) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return;
}
// 到达叶子节点
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
if (root->val == sum) {
path.push_back(root->val);
res.push_back(path);
path.pop_back();
}
return;
}
// 当前节点加到path中
path.push_back(root->val);
// 更新sum,到左右子树中去添加path
int newsum = sum - root->val;
if (root->left) {
find_path(root->left, newsum, path, res);
}
if (root->right) {
find_path(root->right, newsum, path, res);
}
// 当前节点从path中移除
path.pop_back();
}题目3 求二叉树的所有和为sum的路径,任意起始节点-437
给一颗二叉树和sum,求出所有和为sum的路径数量,从任意节点开始和结束。
思路
- 层次遍历,以每一颗节点为起始值,找到以它开始的路径数量
- 节点为空,0
- 无孩子,不相等,0
- 无孩子,相等,1
- 有孩子,相等,
c = 1, 不相等c = 0。 更新sum,继续递归查找左右孩子的count。返回c+count
/*
* 找到树中,和为sum的所有路径数量
*/
int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
int count = 0;
// 前序遍历
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* now = q.front();
q.pop();
count += count_from_root(now, sum);
if (now->left) q.push(now->left);
if (now->right) q.push(now->right);
}
return count;
}
/*
* 以root为起始节点,向下走,和为sum的路径的条数
*/
int count_from_root(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
// 空
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
// 直接根节点就满足,无需看孩子
int c = 0;
if (sum == root->val) {
// 相等
c = 1;
} else if (!root->left && !root->right) {
// 无孩子,不相等
return 0;
}
// c+左右孩子的
int newsum = sum - root->val;
return c + count_from_root(root->left, newsum) + count_from_root(root->right, newsum);
}有序链表转平衡BST-109
Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree, Medium。 类似题型:BST转有序双向链表
给一个有序链表,转化为平衡的二叉搜索树
思路
有序 -- BST的中序遍历;平衡 -- 以中间节点为根节点,分为左右子树递归去创建。
- 计算总结点数量 --
size, 递归去构建树go(0, size - 1) go(head, start, end),计算出中间节点mid-node, 构造树根root- 左孩子
root.left = go(head, start, mid-1), 右孩子root.right = go(now.next, mid+1, end) - 返回当前树根节点root
/*
* 把有序链表转化为平衡的BST
* Args:
* head -- 链表
* Returns:
* root -- 树的头结点
*/
TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
int size = 0;
ListNode* p = head;
while (p) {
++size;
p = p->next;
}
return create_tree(head, 1, size);
}
/*
* 递归中序创建树
* Args:
* head -- 链表头节点
* start -- 起始节点编号,从1开始
* end -- 结束节点编号
* Returns:
* root -- 树的根节点
*/
TreeNode* create_tree(ListNode* head, int start, int end) {
// 0. 递归终止条件
if (head == nullptr || start > end) {
return nullptr;
}
// 1. 找到中间节点,构建根节点
int mid = (end + start) / 2;
ListNode* node = head;
for (int i = start + 1; i <= mid; i++) {
node = node->next;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(node->val);
// 2. 递归构造左右子树
root->left = create_tree(head, start, mid - 1);
root->right = create_tree(node->next, mid + 1, end);
return root;
}序列化二叉树-297
Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree, Hard
把二叉树序列化为字符串,把字符串反序列化为一棵树
思路
前序遍历来保存序列,保存成一颗完全二叉树,空节点用$表示,使用空格进行分割。
序列化
- 序列化为一颗完全二叉树,先序递归。遇到空指针,则用
$代替 - 先把字符放到
stringstream里面,<<输入, 最后s.str()得到字符串
/*
* 把一棵树序列化为一个字符串,前序完全二叉树序列
* Args:
* root -- 树
* Returns:
* str -- 序列化后的字符串
*/
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return "";
}
stringstream buf;
build_string(root, buf);
return buf.str();
}
/*
* 递归把二叉树序列化到buf字符串中
* Args:
* root -- 当前的根节点
* buf -- 字符串buffer
* Returns:
* None,都写到了buf中
*/
void build_string(TreeNode* root, stringstream& buf) {
if (root == nullptr) {
buf << "$" << " ";
return;
}
buf << root->val << " ";
build_string(root->left, buf);
build_string(root->right, buf);
return;
}从字符串中解析得到序列,存到队列中
/*
* 分割字符串,把字符写到容器q里面
*/
void split(const string& str, queue<string> &q, const char delim = ' ') {
istringstream input;
input.str(str);
string line;
while (std::getline(input, line, delim)) {
q.push(line);
}
return;
}反序列化
得到队列序列之后,可以对其进行递归反序列化构建树。先序序列,不是层次序列。
- 根-左-右,队列。出队,建立根节点
- 左-右,队列,递归建立左孩子
- 右,队列,建立右孩子
/*
* 把String解析为一棵树
* Args:
* data -- 序列化后的字符串
* Returns:
* root -- 树
*/
TreeNode* deserialize(const string& data) {
if (data.empty()) {
return nullptr;
}
// 先序序列
queue<string> preorder;
split(data, preorder);
return build_tree(preorder);
}
/*
* 递归先序构造树
* Args:
* prev -- 先序遍历序列
* Retursn:
* root -- prev[i]为根构建的树
*/
TreeNode* build_tree(queue<string>& pres) {
if (pres.size() == 0) {
return nullptr;
}
string val = pres.front();
pres.pop();
// 当前为空节点
if (val == "$") {
return nullptr;
}
// 有值
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(std::stoi(val));
// 递归按照顺序构建左右子树
root->left = build_tree(pres);
root->right = build_tree(pres);
return root;
}数字全排列-046
Permutations, Medium。 搜索树
给一个数组,返回全排列。每个数字都不相同
思路
全排列回溯法搜索。一个数组,搜索第t层的时候
- 前面t-1层都已经ok
- 遍历后面的所有元素,给到t层,去搜索
- 每次进行交换
/*
* 数组的全排列
*/
vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int> &nums) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
dfs(nums, 0, res);
return res;
}
/*
* 回溯搜索排列树,遍历当前第i层的所有可能性,前面i-1已经全部确定好
* Args:
* t -- 第几层,[0, n-1]
* path -- 当前路径,[0,i-1]已经确定好,[i,n-1]是剩余的数字,遍历每一种可能给到i
* res -- 总的结果
* Returns:
* None
*/
void dfs(vector<int>& path, int t, vector<vector<int>>& res) {
if (t >= path.size()) {
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
for (int i = t; i < path.size(); i++) {
std::swap(path[t], path[i]);
dfs(path, t + 1, res);
std::swap(path[t], path[i]);
}
}重复数字全排列-047
给一个数组,里面有一些重复的数字,给出所有的排列可能
思路
重复的原因:当为t设置值的时候,遍历后面的所有元素给t赋值,但是后面都有一些重复的数值。
比如说 1 2 1 1, 开始是1,1会与最后的两个1再进行交换,然而其实是一样的。没必要了。
每次遍历交换的时候,只交换遍历后面不重复的元素。
/*
* 回溯搜索排列树,遍历当前第i层的所有可能性,前面i-1已经全部确定好
* Args:
* t -- 第几层,[0, n-1]
* path -- 当前路径,[0,i-1]已经确定好,[i,n-1]是剩余的数字,遍历每一种可能给到i
* res -- 总的结果
* Returns:
* None
*/
void dfs(vector<int>& path, int t, vector<vector<int>>& res) {
if (t >= path.size()) {
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
// 不重复的元素与其索引
set<int> vals;
set<int> idx;
for (int i = t; i < path.size(); i++) {
if (vals.find(path[i]) == vals.end()) {
vals.insert(path[i]);
idx.insert(i);
}
}
for_each(idx.begin(), idx.end(), [&](int i) {
std::swap(path[t], path[i]);
dfs(path, t + 1, res);
std::swap(path[t], path[i]);
});
}组合问题
给n个字符,要组成m个字符,问有多少种组成方法
有点类似于01背包的选择。
- 选择第一个字符,则在后面选择m-1个字符
- 不选择第一个字符,则在后面选择m个字符
正方体顶点和相等问题
给8个数字,正方体有8个顶点,数字放在顶点上。使得3对对面的顶点和相等。
也就是搜索,然后限定一些条件。
8皇后问题
8*8的象棋摆8个皇后,任意两个皇后不能在同一行、同一列或同一对角线上。问有多少种摆法
N皇后问题-051
n*n的棋盘摆n个皇后,任意两个皇后不能在同一行、同一列或同一对角线上。返回摆法。
- 每一行一个皇后,每一行有n个选择。就去dfs搜索所有的排列树。
path[t]=k, 第t行的皇后在第k列- k不能在前面皇后的:同一列、主对角线、副对角线 。别忘记副对角线。
/*
* 返回n皇后的解法
*/
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
// 1. 获得所有可能的位置
vector<vector<int>> locations;
vector<int> path(n);
std::iota(path.begin(), path.end(), 0);
dfs(0, n, path, locations);
// 2. 构造返回结果
vector<vector<string>> res;
for (auto loc : locations) {
vector<string> solu;
for (int i : loc) {
string line(n, '.');
line[i] = 'Q';
solu.push_back(line);
}
res.push_back(solu);
}
show(res[0]);
return res;
}
/*
* dfs,设置t行的皇后位置
* Args:
* t -- 第t行,从0开始
* n -- n皇后
* path -- 当前的路径方案
* res -- 总的方案
* Returns:
* None
*/
void dfs(int t, int n, vector<int>& path, vector<vector<int>>& res) {
if (t == n) {
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
// 前面t-1行已经ok,再后面的t-n个选择中选择遍历t
for (int i = t; i < n; i++) {
if (legal(t, path[i], path) == true) {
swap(path[i], path[t]);
//cout << "t=" << t << ", k=" << path[i] << endl;
//for_each(path.begin(), path.end(), [](int i){cout << i << " ";});
dfs(t + 1, n, path, res);
swap(path[i], path[t]);
}
}
}
/*
* 合法性判断,同一列、主对角线、副对角线
* Args:
* t -- 第t行,从0开始
* k -- 放在第k个列,从0开始
* path -- 当前的路径,[0,t-1]行已经放好
* Returns:
* true or false
*/
bool legal(int t, int k, const vector<int>& path) {
for (int i = 0; i <= t - 1; i++) {
// 1. 不能和之前的在同一列
if (path[i] == k) {
return false;
}
// 2. 不能在主对角线上
if (t - i == k - path[i]) {
return false;
}
// 3. 不能在副对角线上
if (t + k == i + path[i]) {
return false;
}
printf("p[%d]=%d,p[%d]=%d\n", t, k, i, path[i]);
}
return true;
}N皇后问题-052
返回有多少种解法
做了上面的题,那这个就很简单了,返回数量就行了。
/*
* 返回n皇后的解法
*/
int solveNQueens(int n) {
// 所有的结果
vector<vector<int>> locations;
// 当前的位置
vector<int> path(n);
// 初始化为0-n-1
std::iota(path.begin(), path.end(), 0);
// dfs遍历搜索
dfs(0, n, path, locations);
return locations.size();
}查找第k大的数总结
给N个数,确定第k个最大值
1 排序
排好序,取出第k大的值。
2 简单选择排序
简单选择。第k次选择,就是第k大的数字。
3 快速排序思想
每次partition,会把x放到位置i上。注意partition要从大到小排列,左大右小,而不是普通排序的左小右大。
i == k, 则就是a[i]k > i, 则在i的右边k < i, 则在i的左边
[关键代码]
/*
* 使用快排思想查找第k大的数字,从大到小排列!!
* Args:
* a -- 数组
* l -- 范围的开始
* r -- 范围的结束
* k -- 该范围内第k大的数
* Returns:
* 第k大的数
*/
int find_kth_num(vector<int> &a, int l, int r, int k) {
// 1. 划分。左边大,中间a[l],右边小
int i = partition(a, l, r);
// 2. 通过i+1==k来判断是否是第k大的数
if (i + 1 == k) {
return a[i];
} else if (i + 1 > k) {
// 在左边
return find_kth_num(a, l, i - 1, k);
} else {
// 在右边
return find_kth_num(a, i + 1, r, k);
}
}4 最大堆
5 最小堆
维护大小为k的最小堆,遍历数组
- 堆顶元素大,则不管
- 堆顶元素小,则把当前值插入堆中
- 最后的堆顶,就是第k大的元素
6 Hash法
查找最小的k个数的总结
给一个数组,找到最小的k个数。注意改变或不改变原数组
1 排序思路
对n个数字从小到大排好序,再取前k个数。O(nlogn + k)=O(nlogn) 。排序算法总结
2 快速排序
排好前k个即可,改变原数组。
3 最大堆
建立大小为k的最大堆。不改变原数组。遇到新的元素,小于堆顶,则加入
4 堆排序
对整个数组n进行堆排序,每次取堆顶,取k次。
数组中次数超过一半的数-169
Majority Element-169, easy
一个数组,有一个元素出现次数超过一半,找到它。
思路0 先排序再找
思路1 快速排序查找第k大元素思想
快速排序笔记 。
- 如果排好序,则该重复的数字应该在数组中间
。 也就是中位数,第 n/2大的数字 - 问题就转化为查找数组中的K大的元素
查找第k大的元素
partition(a, l, r)会把x=a[l]放到中间去,小于的在右边,大于的在左边。返回x的最终位置ii == k, 则x就是第k大的元素k < i, 则k在右边k > i, 则k在左边- 继续查找,知道
i == k
思路2 count加加减减思想
- 遇见友军(相同的),就++
- 遇见敌军(不同的),就--
- 最后剩余的肯定就是人数最多的那个(数字)
[关键代码]
/*
* 查找主元素,阵地攻守思想。相同加价,不同减减,为0重新赋值
*/
int majority_element(vector<int>& a) {
if (a.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
// 当前数值与计数
int res = a[0];
int count = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < a.size(); i++) {
if (a[i] == res) {
// 相同++
count++;
} else {
// 不同--或者重置为1
if (count == 0) {
res = a[i];
count = 1;
} else {
count--;
}
}
}
return res;
}主元素2-229
给一个数组,找到所有出现次数超过n/3的数
Majority Element II, medium 。
思路
当然最终结果只有2个或1个。思路同阵地攻守。
- 用两个变量去记录两个主元素
- 有一个相同,对应加1
- 两个都不同,有一个
count==0, 则重置 - 两个都不听,两个都有count,则都减减
- 遍历之后,得到两个数,两个count
- 返回
count > n/3的数
最后,一定要注意去重!n1 != n2
/*
* 查找出现次数超过n/3的元素
* Args:
* nums -- 数组
* Returns:
* res -- 超过n/3的元素
*/
vector<int> majority_element(const vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> res;
if (nums.empty()) {
return res;
}
// 1. 找到出现次数最多的两个数
int n1 = 0, c1 = 0;
int n2 = 0, c2 = 0;
for (int n : nums) {
if (n == n1) {
c1++;
} else if (n == n2) {
c2++;
} else if (c1 == 0) {
n1 = n;
c1 = 1;
} else if (c2 == 0) {
n2 = n;
c2 = 1;
} else {
c1--;
c2--;
}
}
c1 = 0, c2 = 0;
// 2. 重新计算出现次数
for (auto n : nums) {
if (n1 == n) {
c1++;
} else if (n2 == n) {
c2++;
}
}
// 3. 把出现次数超过n/3的数字放到res里面
if (c1 > nums.size() / 3) {
res.push_back(n1);
}
// 去重
if (n2 != n1 && c2 > nums.size() / 3) {
res.push_back(n2);
}
return res;
}最长不重复子字符串-003
Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters-003
给一个字符串,找到里面最长子字符串的长度。
1 DP思路
设l[i]=k, 是以s[i]结尾最长字符串的长度是k。从左到右进行计算。遍历到s[i]
1、 s[i]在前面没有出现过,l[i] = l[i-1] + 1
2 、s[i]在前面出现过,计算该字符现在与前面两次出现的距离d,比较d和s[i-1]的最大长度l[i-1]
d > l[i-1], d很远(不在i-1的最长字符串里),l[i] = l[i-1] + 1d <= l[i-1],d很近(在i-1的最长字符串里),l[i]=d
使用HashMap<Char, Int>去记录位置信息,保留最近时间的出现位置。
/*
* 字符串中,最长不重复子串的长度,是连续
* Args:
* s -- 原字符串
* Returns:
* len -- 最长子串长度
*/
int long_substr_len(const string& s) {
if (s.empty()) {
return 0;
}
// 长度,l[i]=k,以s[i]结尾的最大子串长度为k
vector<int> l(s.length(), 0);
// 位置,m['a']=i,最近,字符a出现的位置是i
map<char, int> m;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char ch = s[i];
if (i == 0) {
l[i] = 1;
m[ch] == i;
continue;
}
if (m.find(ch) == m.end()) {
// ch 没出现过
l[i] = l[i-1] + 1;
} else {
// ch 出现过,距离比较
int d = i - m[ch];
if (d > l[i-1]) {
// 上一个ch距离很远
l[i] = l[i-1] + 1;
} else {
// 上一个ch距离很近
l[i] = d;
}
}
// 更新出现位置
m[ch] = i;
}
return *max_element(l.begin(), l.end());
}丑数-263-264-313
263-判断是否是丑数 ,easy
只包含2、3、5作为因子的正整数是丑数,1也是。判断是否是丑数
bool isUgly(int num) {
// 特殊情况
if (num <= 0) {
return false;
}
if (num == 1) {
return true;
}
// 不断分解2,3,5
vector<int> a = {2, 3, 5};
for (auto i : a) {
while (num % i == 0) {
num /= i;
}
}
return num == 1;
}264-找到第n个丑数 ,medium
找到第n个丑数
如果依次找,所有的数都要分解求余,效率低。丑数=丑数*(2,3,5)。 用数组去存放丑数,从1开始依次向前面递推计算。
用3个索引,去分别保存乘以2,3,5的基数,每次选择最小的作为下一个丑数,同时更新对应的索引++。
/*
* 第n个丑数,从已有的丑数不断地向前乘得到新的丑数。
*/
int nthUglyNumber(int n) {
if (n <= 0) {
return -1;
}
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
vector<int> u(n);
u[0] = 1;
int t2 = 0, t3 = 0, t5 = 0;
// 计算丑数
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// 计算新的丑数,选择最小的
int cur = min(min(u[t2] * 2, u[t3] * 3), u[t5]*5);
u[i] = cur;
// 更新基数索引
if (cur == u[t2] * 2) {
t2++;
}
if (cur == u[t3] * 3) {
t3++;
}
if (cur == u[t5] * 5) {
t5++;
}
}
return u[n-1];
}313-超级丑数, medium
超级丑数是,给一个素数列表去计算丑数,不再局限于2,3,5去计算丑数。
给一个素数列表和n,返回第n个丑数
和上一个思路一致,用数组保存。注意t数组的初始大小是primes.size(),而不是n。
/*
* 给定素数,返回第n个丑数
*/
int nthSuperUglyNumber(int n, vector<int>& primes) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
if (n <= 0 || primes.empty()) {
return -1;
}
vector<int> u(n);
u[0] = 1;
vector<int> t(primes.size(), 0);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
// 计算新的丑数,选择最小的
int cur = INT_MAX;
for (int j = 0; j < primes.size(); ++j) {
cur = min(cur, u[t[j]] * primes[j]);
}
u[i] = cur;
// 更新索引,向前推进
for (int j = 0; j < primes.size(); ++j) {
if (cur == u[t[j]] * primes[j]) {
t[j]++;
}
}
}
return u[n-1];
}